The Future is Generative: Key Applications of AI in Modern Technology
Digital content creation and interaction have been revolutionized by generative AI, which has swept the IT industry. Even though this technology has a wide range of possible uses, text-based applications account for a significant portion of its usage. The primary uses of generative AI, such as audio, conversational, data augmentation, and video/visual applications, will be discussed in this blog post, along with the reasons behind their dominance in text applications.
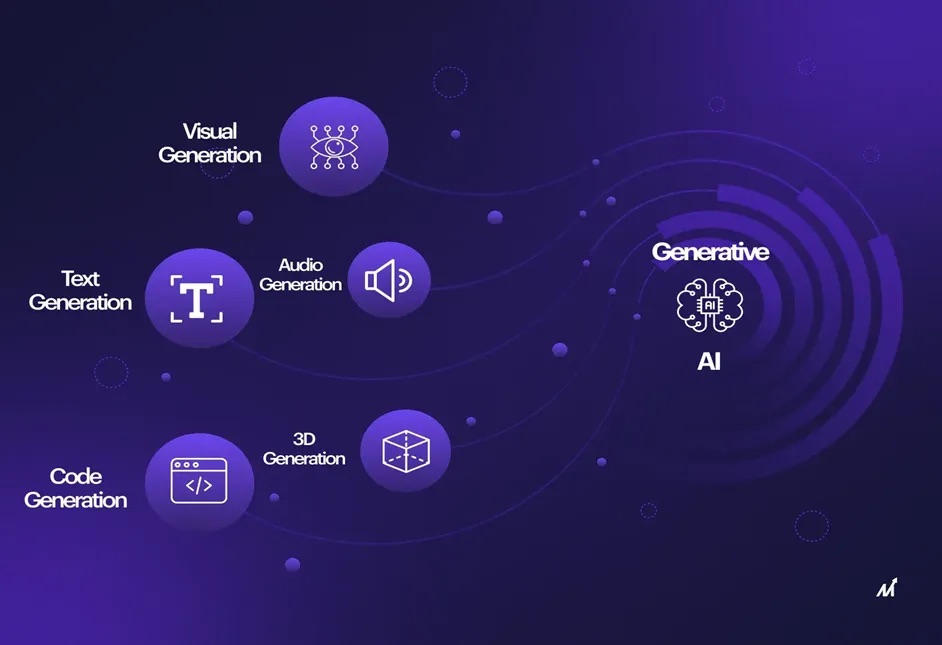
1. Text Applications
Perhaps the most developed and often used use case for generative AI is in text applications. This covers jobs like writing summaries, translating between languages, and creating content. There are several factors contributing to text applications’ dominance:
Historical Data Availability: Text data is widely available, well-documented, and a valuable resource for AI model training.
Measures for Clear Evaluation: Text applications frequently feature well-defined success measures (such as coherence and grammar accuracy), making the process of training and assessing models easier.
Broad Applicability: Text production is useful in a variety of fields, including marketing, customer service, journalism, and education.
Key Examples:
Content Creation: Tools like OpenAI’s GPT series have revolutionized how articles, blog posts, and even books are written.
Language Translation: AI-powered translation tools have made cross-language communication seamless and efficient.
Text Summarization: AI can condense lengthy documents into concise summaries, saving time and enhancing productivity.

2. Audio Applications
The audio applications of generative AI are centered on producing, altering, and refining sound. This covers the creation of sound effects, voice synthesis, and music composition.
Key Examples:
Content Creation: Tools like OpenAI’s GPT series have revolutionized how articles, blog posts, and even books are written.
Voice Synthesis: Text-to-speech (TTS) systems can generate natural-sounding human speech, useful in audiobooks, virtual assistants, and more.
Sound Effects: AI can create realistic sound effects for movies, video games, and virtual reality experiences.
3. Conversational Applications
Conversational apps use artificial intelligence (AI) to provide more intuitive and natural interactions between people and machines. Chatbots, virtual assistants, and customer service frequently use these apps.
Key Examples:
Chatbots : AI chatbots instantly respond to questions from customers, increasing the effectiveness of customer support.
Virtual Assistants: Artificial intelligence (AI) is used by virtual assistants such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant to recognize and react to spoken instructions.
Interactive Storytelling: AI-powered systems for storytelling generate dynamic stories in response to user input.
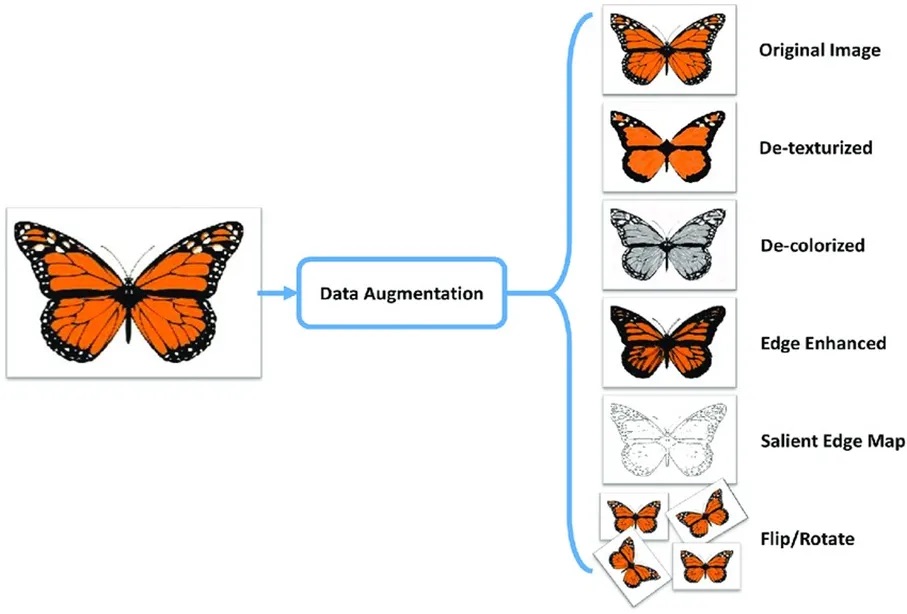
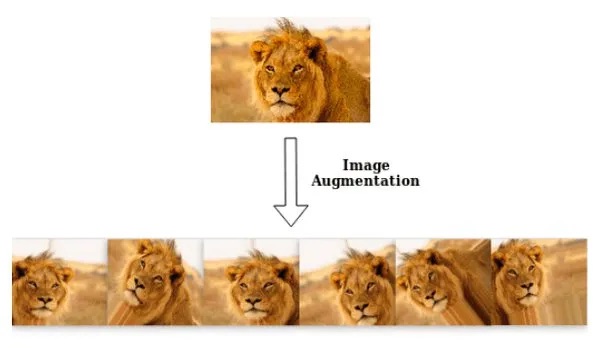
4. Data Augmentation
AI is used in data augmentation to increase and improve already-existing datasets, which is essential for building stronger machine learning models. This is especially crucial in industries where obtaining data is expensive or difficult.
Key example:
Image Augmentation: To enhance computer vision model training, generative AI can produce different images.
Text Data Augmentation: Artificial intelligence (AI) can produce extra text data, such as paraphrases or enlarged datasets for uncommon languages, to train natural language processing (NLP) models.
Synthetic Data Generation: Artificial intelligence (AI) creates synthetic data that imitates real-world data while protecting privacy in situations like medical research.
5. Code generation:
Code generation is one use of generative AI, wherein AI models are used to independently produce code according to requirements or needs. For developers in particular, this program can generate template code, automate repetitive coding activities, and even help with debugging and reworking code. An example of how to create a generative AI code generation application using a fictional AI model is provided here, along with an outline of the process:
Key example:
Below is a simplified example implementation of a code generation application using OpenAI’s GPT-3 model (assuming you have access to the GPT-3 API):
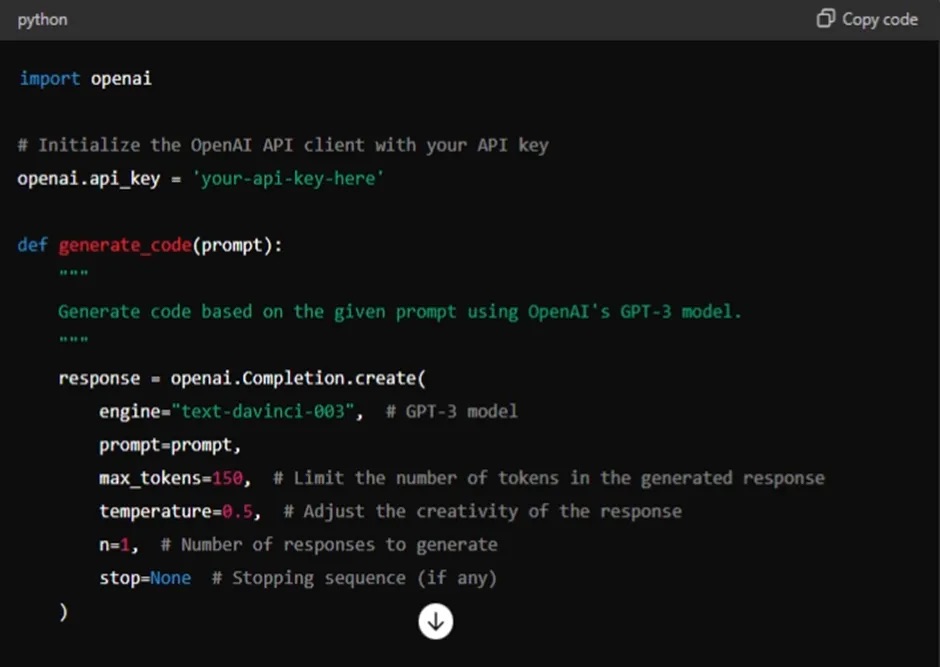
Explanation of API Initialization: The supplied API key is used to initialize the Open AI API.
Generate Code Function Definition: The definition of a function is to produce code in response to an input. With the prompt and additional parameters like max tokens (to restrict the length of the response), temperature (to govern creativity), and n (number of responses), the function submits a request to the Open AI API.
Give An Example A defined prompt asks the model to produce a Python code that finds a number’s factorial.
Code Generation: The generated code is printed once the function is called with the prompt.
Conclusion
The potential of generative AI in text applications is only beginning to be realized. For historical, pragmatic, and technological reasons, text is still the most used domain; nevertheless, the other domains — audio, conversational, data augmentation, and video/visual — are developing quickly. Because generative AI has the potential to revolutionize many aspects of digital content creation and interaction, each application area has its own set of opportunities and constraints. We may anticipate much more inventive and varied applications to arise as technology develops, further incorporating AI into our daily lives.
